Dual-polarized Slot Antenna For Millimeter Waves
Musavand, et al., “A compact UWB slot antenna with reconfigurable band-notched function for multimode applications,” Appl Comp Electromagn Soc J, vol. Ullah, et al., “Coplanar waveguide antenna with defected ground structure for 5G millimeter wave communications,” IEEE MENACOMM'19, Bahrain, 2019. We propose a dual-polarized lens antenna system based on isotropic metasurfaces for 12 GHz applications. The metasurface lens is composed of subwavelength unit cells (0.24 λ 0 ) with metallic strips etched on the top and bottom sides of the unit cell, and a cross-slots metallic layer in the middle that serves as the ground.
Authors:Raed A. Abd-Alhameed, Naser Ojaroudi Parchin, Haleh Jahanbakhsh Basherlou, Peter S. Excell
Abstract:

In this paper, a multiple-input/multiple-output (MIMO) antenna design with polarization and radiation pattern diversity is presented for future smartphones. The configuration of the design consists of four double-fed circular-ring antenna elements located at different edges of the printed circuit board (PCB) with an FR-4 substrate and overall dimension of 75×150 mm2. The antenna elements are fed by 50-Ohm microstrip-lines and provide polarization and radiation pattern diversity function due to the orthogonal placement of their feed lines. A good impedance bandwidth (S11 ≤ -10 dB) of 3.4-3.8 GHz has been obtained for the smartphone antenna array. However, for S11 ≤ -6 dB, this value is 3.25-3.95 GHz. More than 3 dB realized gain and 80% total efficiency are achieved for the single-element radiator. The presented design not only provides the required radiation coverage but also generates the polarization diversity characteristic.
Keywords:MIMO Systems, polarization diversity, cellular communications, mobile-phone antenna
Digital Object Identifier (DOI):doi.org/1
ProcediaAPABibTeXChicagoEndNoteHarvardJSONMLARISXMLISO 690PDF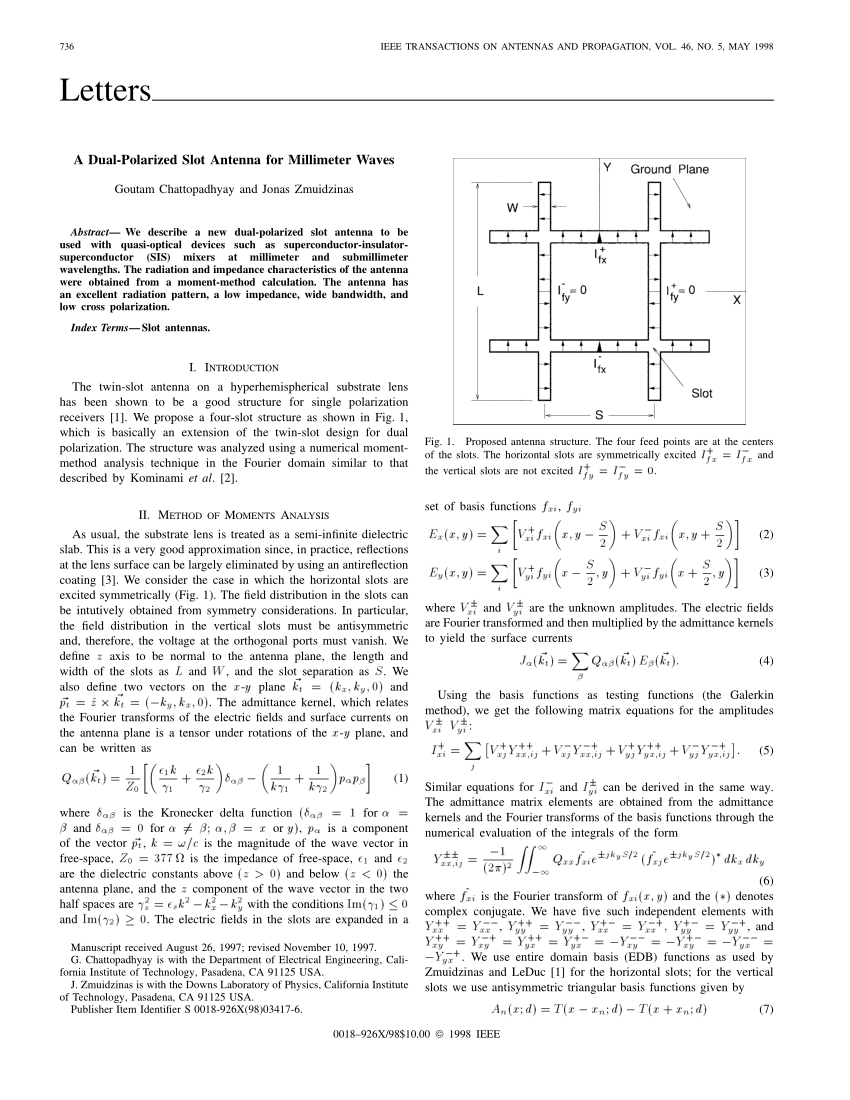 Downloads 256
Downloads 256References:
[1] M. S. Sharawi, “Printed MIMO antenna engineering,” Norwood, MA, USA: Artech House, 2014.
[2] N. O. Parchin, et al., “8×8 MIMO antenna system with coupled-fed elements for 5G handsets,” The IET Conference on Antennas and Propagation (APC), 11-12 November, 2019, Birmingham, UK.
[3] N. O. Parchin, et al., “Dual-polarized MIMO antenna array design using miniaturized self-complementary structures for 5G smartphone applications,” EuCAP Conference, Krakow, Poland, 2019.

[4] N. Ojaroudi et al., “Design of CPW-fed slot antenna for MIMO system applications,” Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett., vol. 56, pp. 1278-1281, 2014.
[5] A. Osseiran, et al., “Scenarios for 5G mobile and wireless communications: the vision of the METIS project,” IEEE Commun. Mag., vol. 52, pp.26-35, 2014.
[6] Q.U.A. Nadeem, et al., “Design of 5G full dimension massive MIMO systems,” IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 66, pp. 726–740, 2018.
[7] N. Ojaroudiparchin, et al., “Multi-layer 5G mobile phone antenna for multi-user MIMO communications,” TELFOR 2015, Nov.2015, Serbia.
[8] N. O. Parchin, et al., “MM-wave phased array quasi-yagi antenna for the upcoming 5G cellular communications,” Applied Sciences, vol. 9, pp. 1-14, 2019.
[9] N. Ojaroudi, et al., “An omnidirectional PIFA for downlink and uplink satellite applications in C-band,” Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, vol. 56, pp. 2684-2686, 2014.
[10] Y.-L. Ban, et al., “4G/5G multiple antennas for future multi-mode smartphone applications,” IEEE Access, vol. 4, pp. 2981–2988. 2016.
[11] P. Gupta, “Evolvement of mobile generations: 1G to 5G,” International Journal for Technological Research in Engineering, vol. 1, pp. 152-157, 2013.
[12] N. Ojaroudi, “Design of microstrip antenna for 2.4/5.8 GHz RFID applications,” GeMic 2014, RWTH Aachen University, Germany, 2014.
[13] N. Ojaroudi, “Circular microstrip antenna with dual band-stop performance for ultra-wideband systems,” Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett., vol. 56, pp. 2095-2098, 2014.
[14] N. Ojaroudi, et al., “Very low profile ultrawideband microstrip band-stop filter,” Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett., vol. 56, pp. 709-711, 2014.
[15] N. O. Parchin, et al., “Mobile-phone antenna array with diamond-ring slot elements for 5G massive MIMO system,” Electronics, vol. 9, pp. 1-14, 2019.
[16] N. Ojaroudi, et al., “Compact ultra-wideband monopole antenna with enhanced bandwidth and dual band-stop properties,” International Journal of RF and Microwave Computer-Aided Engineering, vol. 25, pp. 346–357, 2015.
 [17] M.-Y. Li, et al., “Tri-polarized 12-antenna MIMO array for future 5G smartphone applications,” IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 6160–6170, 2018.
[17] M.-Y. Li, et al., “Tri-polarized 12-antenna MIMO array for future 5G smartphone applications,” IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 6160–6170, 2018. [18] R. Hussain, et al., “4-element concentric pentagonal slot-line-based ultra-wide tuning frequency reconfigurable MIMO antenna system,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., vol. 66, pp. 4282–4287, 2018.
[19] M. Abdullah, et al., “Eight-element antenna array at 3.5GHz for MIMO wireless application,” PIER C, vol. 78, pp. 209-217, 2017.
[20] Y. Li, et al., “High-isolation 3.5-GHz 8-antenna MIMO array using balanced open slot antenna element for 5G smartphones,” IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., 2019, doi:10.1109/TAP.2019.2902751.
[21] Statement: Improving Consumer Access to Mobile Services at 3.6 GHz to 3.8 GHz. Available online: https://www.ofcom.org.uk/consultations-and-statements/category-1/future-use-at-3.6-3.8-ghz.
[22] N. Ojaroudi, et al., “Enhanced bandwidth of small square monopole antenna by using inverted U-shaped slot and conductor-backed plane,” ACES Journal, vol. 27, 685– 690, 2012.
[23] N. O. Parchin et al., “Multi-band MIMO antenna design with user-impact investigation for 4G and 5G mobile terminals, Sensors, vol. 19, pp. 1-16, 2019.
[24] CST Microwave Studio, ver. 2017, CST, Framingham, MA, USA, 2017.
[25] N. O. Parchin, “Low-profile air-filled antenna for next generation wireless systems,” Wireless Personal Communications, vol. 97, pp. 3293–3300, 2017.
[26] P. Salonen, et al., “A small planar inverted-F antenna for wearable applications”, IEEE International Symposium on Wearable Computers, pp. 96- 100, 1999.
[27] A. Zhao, R. Zhouyou, “Size reduction of self-isolated MIMO antenna system for 5G mobile phone applications,” IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, vol. 18, pp. 152-156, 2019.
Dual-polarized Slot Antenna For Millimeter Waves Frequency
[28] N. Ojaroudi, “Design of ultra-wideband monopole antenna with enhanced bandwidth,” 21th Telecommunications Forum, TELFOR 2013, 27 – 28 November, 2013, Belgrade, Serbia.[29] A. Musavand, et al., “A compact UWB slot antenna with reconfigurable band-notched function for multimode applications,” Appl Comp Electromagn Soc J, vol. 31, pp. 14-18, 2016.
[30] A. Ullah, et al., “Coplanar waveguide antenna with defected ground structure for 5G millimeter wave communications,” IEEE MENACOMM'19, Bahrain, 2019.
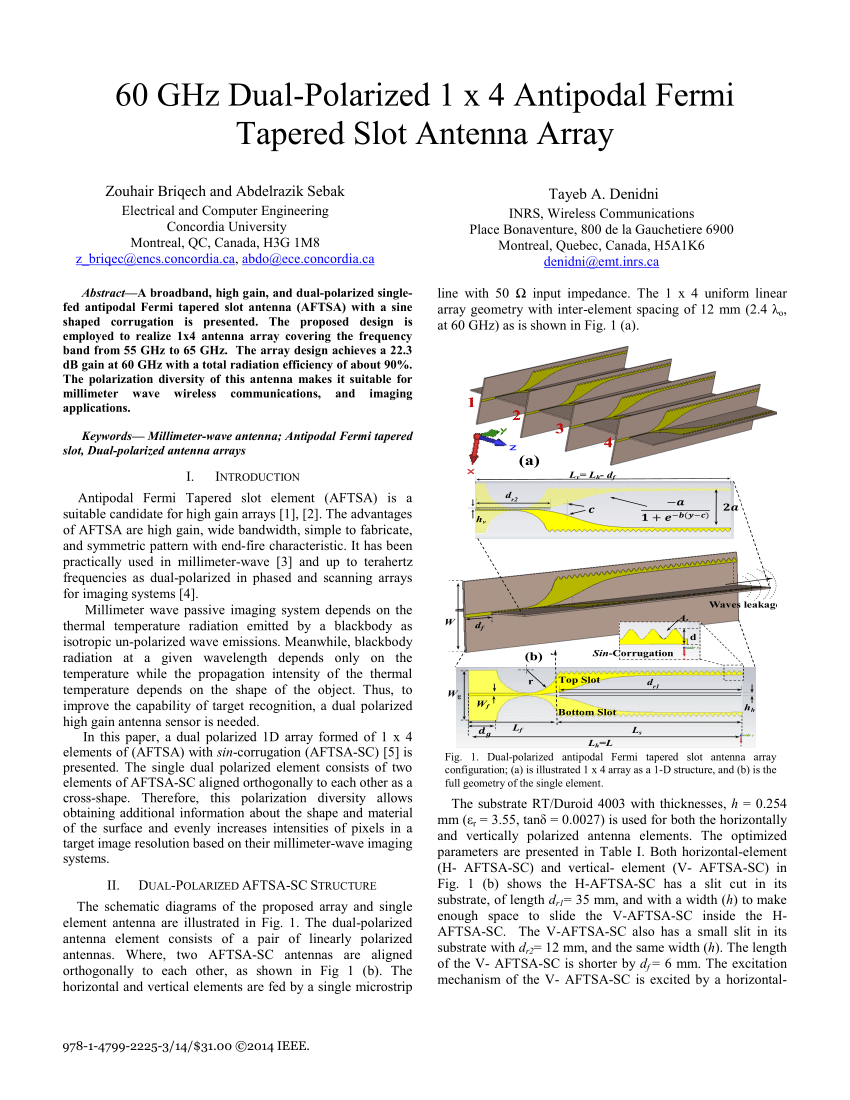
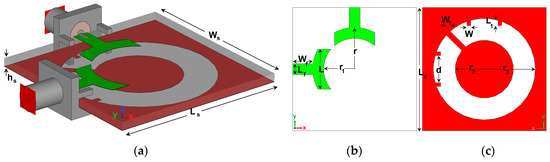
Dual Polarized Slot Antenna
- E.E.M. Woestenburg, L. Bakker, M.V. Ivashina, Experimental results for the sensitivity of a low noise aperture array tile for the SKA. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 60(2), 915–921 (2012)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- D.M. Pozar, S.M. Duffy, A dual-band circularly polarized aperture-coupled stacked microstrip antenna for global positioning satellite. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 45(11), 1618–1625 (1997)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- A. Perron, T. Denidni, A. Sebak, Circularly polarized microstrip/elliptical dielectric ring resonator antenna for millimeter-wave applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 9, 783–786 (2010)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- Y. Dong, H. Toyao, T. Itoh, Compact circularly-polarized patch antenna loaded with metamaterial structures. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 59(11), 4329–4333 (2011)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- Z. Wang, S. Fang, S. Fu, S. Jia, Single-fed broadband circularly polarized stacked patch antenna with horizontally meandered strip for universal UHF RFID applications. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 59(4), 1066–1073 (2011)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- H. Chen, Y. Wang, Y. Lin, C. Lin, S. Pan, Microstrip-fed circularly polarized square-ring patch antenna for GPS applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 57(4), 1264–1267 (2009)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- Y. Zhou, C. Chen, J. Volakis, Single-fed circularly polarized antenna element with reduced coupling for GPS arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 56(5), 1469–1472 (2008)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- S. Yang, K. Lee, A. Kishk, K. Luk, Design and study of wideband single feed circularly polarized microstrip antennas. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 80, 45–61 (2008)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- W. Kim, N. Moon, H. Kim, Y. Kim, Linear polarization sum imaging in passive millimeter-wave imaging system for target recognition. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 136, 175–193 (2013)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- A. Duric, A. Magun, A. Murk, C. Matzler, N. Kampfer, The fully polarimetric imaging radiometer SPIRA at 91GHz. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 46, 2323–2336 (2008)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- O. Stahli, C. Matzler, A. Murk, N. Kampfer, Sky measurements with the imaging polarimeter SPIRA at 91GHz, in 2010 11th Specialist Meeting on Microwave Radiometry and Remote Sensing of the Environment, pp. 181–186, Mar 2010Google Scholar
- E. Altshuler, R. Marr, A comparison of experimental and theoretical values of atmospheric absorption at the longer millimeter wavelengths. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. AP-36(10), 1471–1480 (1988)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- C. Liu, Y. Guo, X. Bao, S. Xiao, 60-GHz LTCC integrated circularly polarized helical antenna array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 60(3), 1329–1335 (2012)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- S. Lin, Y. Lin, A compact outer-fed leaky-wave antenna using exponentially tapered slots for broadside circularly polarized radiation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 60(6), 2654–2661 (2012)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- A. Narbudowicz, X. Bao, M. Ammann, H. Shakhtour, D. Heberling, Circularly polarized antenna with steerable dipole-like radiation pattern. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 62(2), 519–526 (2014)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- Q. Lai, C. Fumeaux, W. Hong, R. Vahldieck, 60 GHz aperture-coupled dielectric resonator antennas fed by a half-mode substrate integrated waveguide. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 58(6), 1856–1864 (2010)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- A. Guntupalli, K. Wu, 60-GHz circularly polarized antenna array made in low-cost fabrication process. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett 13, 864–867 (2014)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- S. Ladan, A. Guntupalli, K. Wu, A high-efficiency 24 GHz rectenna development towards millimeter-wave energy harvesting and wireless power transmission. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 61(12), 3358–3366 (2014)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- J. Gomez-Tornero, D. Blanco, E. Rajo-Iglesias, N. Llombart, Holographic surface leaky-wave lenses with circularly-polarized focused near-fields—Part I: concept, design and analysis theory. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 61(7), 3475–3485 (2013)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- K.S. Yngvesson, T.L. Korzeniowski, Y.S. Kim, E.L. Kollberg, J.F. Johansson, The tapered slot antenna—A new integrated element for millimeter wave applications. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Tech. 37, 365–374 (1989)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- K. Sawaya, H. Sato, Y. Wagatsuma, K. Mizuno, Broadband fermi antenna and its application to mm-wave imaging, in Proceedings of 2nd European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Edinburgh, Nov 2007Google Scholar
- B. Veidt, G.J. Hovey, T. Burgess, R.J. Smegal, R. Messing, A.G. Willis, A.D. Gray, P.E. Dewdney, Demonstration of a dual-polarized phased-array feed. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 59, 2047–2057 (2011)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- H. Holter, T.-H. Chio, D.H. Schaubert, Experimental results of 144-element dual-polarized endfire tapered-slot phased arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 48, 1707–1718 (2000)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- A. Guntupalli, K. Wu, Frequency-steered directive beam with dual circular polarization and two-dimensional scan capability for millimeter-wave imaging and sensing systems, in 2014 IEEE 15th Annual Wireless and Microwave Technology Conference (WAMICON), 2014Google Scholar
- S. Karamzadeh, M. Kartal, Circularly polarised MIMO tapered slot antenna array for C-band application. Electron. Lett. 51(18), 1394–1396 (2015)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- A. Guntupalli, K. Wu, Polarization-agile millimeter-wave antenna arrays, in Microwave Conference Proceedings (APMC), 2012 Asia-Pacific, IEEE, 2012, pp. 148--150Google Scholar
- Z. Briqech, A. Sebak, T.A. Denidni, High gain 60 GHz antipodal fermi tapered slot antenna with sine corrugation. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 57(1), 6–9 (2015)CrossRefGoogle Scholar
- S. Sugawara, Y. Maita, K. Adachi, K. Mori, K. Mizuno, Characteristics of a mm-wave tapered slot antenna with corrugated edges. IEEE MTT-S Int. Microwave Symp. Digest 2, 533–536 (1998)Google Scholar
- Z. Briqech, A. Sebak, T.A. Denidni, Low-cost wideband mm wave phased array using the piezoelectric transducer for 5G applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., intended for the Special Issue on “Antennas and Propagation Aspects of 5G Communications,” submitted in 2016Google Scholar
- F. Yang, Y. Rahmat-Samii, Electromagnetic Band Gap Structures in Antenna Engineering (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2009)Google Scholar
- A. Elboushi, Z. Briqech, A. Sebak, 4-elements MMW array with EBG feeding network, in Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium (APSURSI), IEEE, pp. 162–163, 7–13 July 2013Google Scholar