Delay Slot Instruction
- Branch Delay Slots are one of the awkward features of RISC architectures. RISC CPUs are pipelined by definition, so while the current instruction is in execution, the following instruction (s) will be in the pipeline already.
- – From before branch instruction – From target address: only valuable when branch taken – From fall through: only valuable when branch not taken – Canceling or nullifying branches allow more slots to be filled (non-zero cycle penalty, its value depends on the rate of correct predication) – the delay-slot instruction is turned into a.
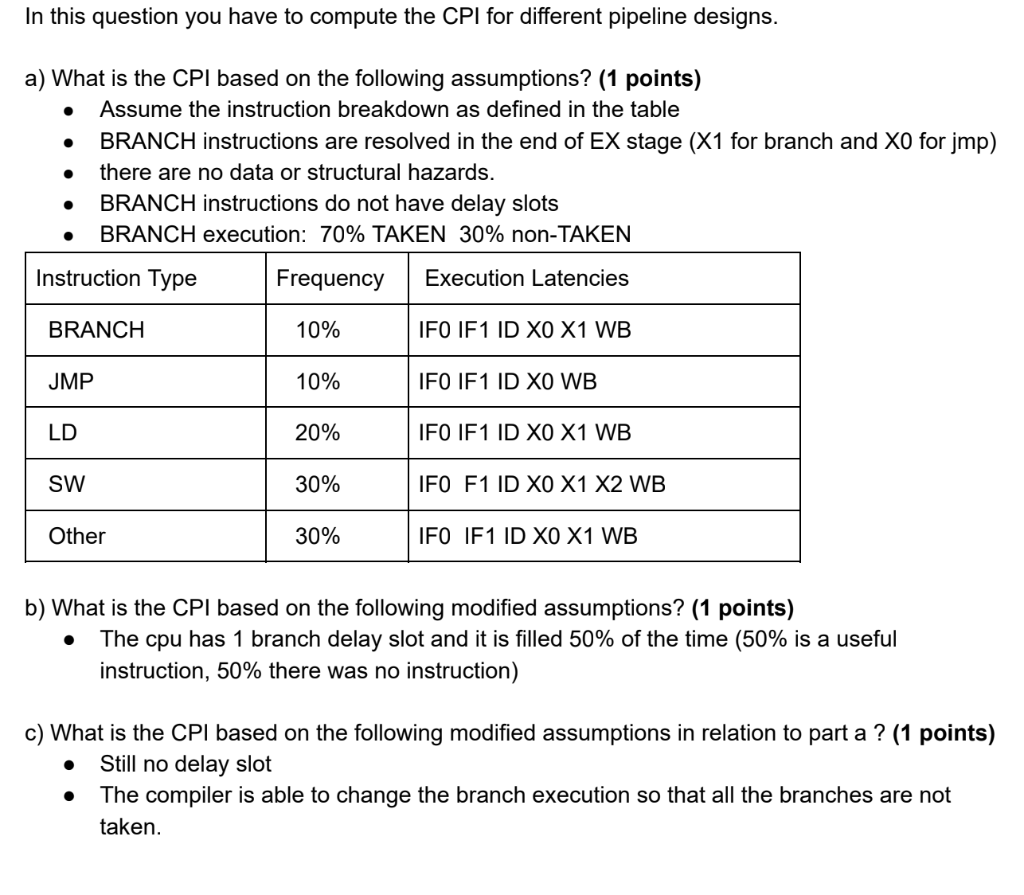
Without delay slot, all juniors to the mispredicted branch are flushed and the branch himself is removed by changing WP in ROB to the ROB tag of the mispredicted branch. With one delay slot declared, the mispredicted branch and the next instruction in branch delay slot have to stay in the ROB. 1 Delay Slots A machine has a ve-stage pipeline consisting of fetch, decode, execute, mem and write-back stages. The machine uses delay slots to handle control dependences. Jump targets, branch targets and destinations are resolved in the execute stage.
Stallpipeline
Predicttaken
Predictnot taken
Delayedbranch
Stall pipeline
The simplest scheme to handle branches is to freezeor flush the pipeline, holdingor deleting any instructions after the branch until the branch destinationis known.
Advantage: simple both to software and hardware (solutiondescribed earlier)
Predict Not Taken
A higher performance, and only slightly more complex, scheme is to predictthe branch as not taken, simply allowing the hardware to continueas if the branch were not executed. Care must be taken notto change the machine state until the branch outcome is definitely known.
The complexity arises from:
wehave to know when the state might be changed by an instruction;
wehave to know how to 'back out' a change.
The pipeline with this scheme implemented behaves as shown below:
| UntakenBranch Instr | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Instr i+1 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Instr i+2 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| TakenBranch Instr | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Instr i+1 | IF | idle | idle | idle | idle |
| Branch target | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Branch target+1 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
Predict Taken
An alternative scheme is to predict the branch as taken. As soon asthe branch is decoded and the target address is computed, we assume thebranch to be taken and begin fetching and executingat the target address.
Because in DLX pipeline the target address is not known any earlier than the branch outcome, there is no advantage in this approach.In some machines where the target address is known before the branchoutcome a predict-taken scheme might make sense.
Delayed Branch
Delay Slot Instruction Mips
In a delayed branch, the execution cycle with a branch delay of lengthn is
Branch instrSequential successors are in the branch-delayslots. These instructions are executed whether or not thebranch is taken.The pipeline behavior of the DLX pipeline, which has one branch delayslot is shown below:
sequential successor 1
sequential successor 2
. . . . .
sequential successor n
Branch target if taken
| Untakenbranch instr | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Branch delay instr(i+1) | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Instr i+2 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Instr i+3 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Instr i+4 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Takenbranch instr | IF | ID | Branch delay instr(i+1) | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Branch target | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB | |||
| Branch target+1 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB | |||
| Branch target+2 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
The job of the compiler is to make the successor instructions validand useful.
We will show three branch-scheduling schemes:

Frombefore branchrestrictions on the instructionsthat are scheduled into the delay slots and
Fromtarget
Fromfall through
ourability to predictat compile time whether a branch is likely to be taken ornot.
CancellingBranch
To improve the ability of the compiler to fill branch delay slots, mostmachines with conditional branches have introduced aMips Branch Delay Slot Instruction
cancellingbranch. In a cancelling branch the instruction includesthe direction that the branch was predicted.- if the branch behaves as predicted, the instruction in the branchdelay slot is fully executed;
- if the branch is incorrectly predicted, the instruction in the delayslot is turned into no-op(idle
 ).
).The behavior of a predicted-taken cancellingbranch depends on whether the branch is taken or not:
| Untakenbranch instr | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Branch delay instr(i+1) | IF | ID | idle | idle | idle |
| Instr i+2 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Instr i+3 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Instr i+4 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Takenbranch instr | IF | ID | Branch delay instr(i+1) | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
| Branch target | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB | |||
| Branch target+1 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB | |||
| Branch target+2 | IF | ID | EX | MEM | WB |
Delay Slot Instructions
The advantage of cancellingbranches is that they eliminate the requirements on theinstructionplaced in the delay slot.
Branch Delay Slot Instruction
Delayed branches are an architecturallyvisible feature of the pipeline. This is the source both of their advantage- allowing the use of simple compiler scheduling to reduce branch penalties;and
their disadvantage - exposingan aspect of the implementation that is likely to change.